浅谈ASP.NET的Postback 实例代码 |
|
本文标签:ASP.NET,Postback 我们知道,无论是ASP.NET1.x,2.0,甚至是以后的版本,ASP.NET最终Render到Client端通过浏览器浏览的都是一样:一个单纯的HTML 。Client通过Submit Form的方式将填入Form的数据提交给Server进行处理 。我们现在来看看ASP.NET整个Postback程序处理的过程 。 首先我们通过一个Sample来看ASP.NET如何处理一个通过Click一个Button引起的Postback 。下面是Web Page的HTML: 复制代码 代码如下: <%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeFile="Default.aspx.cs" Inherits="_Default" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head runat="server"> <title>Test Page</title> </head> <body> <form id="form1" runat="server"> <div> <asp:Label runat="server" ID="LabelMessage" ForeColor="red"></asp:Label> </div> <div> <asp:Button runat="server" ID="Button1" Text="Button1" OnClick="Button1_Click" OnCommand="Button_Command" CommandArgument="Button1" /> <asp:Button runat="server" ID="Button2" Text="Button2" OnClick="Button2_Click" OnCommand="Button_Command" CommandArgument="Button2" UseSubmitBehavior="false" /> <asp:Button runat="server" ID="Button3" Text="Button3" OnClick="Button3_Click" OnCommand="Button_Command" CommandArgument="Button3" UseSubmitBehavior="false" /> </div> </form> </body> </html> 很简单,定义了3个Button,分别注册了他们的两个Event:Click和Command 。3个Button的Command Event Hander是一样的:Button_Command,通过指定的CommandArgument来让Event Handler判断到底是哪个Button触发了Command Event 。 下面是Code Behind: 复制代码 代码如下: using System; using System.Data; using System.Configuration; using System.Web; using System.Web.Security; using System.Web.UI; using System.Web.UI.WebControls; using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts; using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls; public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page { protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { } protected void Button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string message = string.Format("The {0} event of {1} is fired", "Click", "Button1"); this.LabelMessage.Text = message; } protected void Button2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string message = string.Format("The {0} event of {1} is fired", "Click", "Button2"); this.LabelMessage.Text = message; } protected void Button3_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { string message = string.Format("The {0} event of {1} is fired", "Click", "Button3"); this.LabelMessage.Text = message; } protected void Button_Command(object sender, CommandEventArgs e) { string message = string.Format("The {0} event of {1} is fired", "Command", e.CommandArgument); this.LabelMessage.Text += "; " + message; } } 我们来运行这个Page,并Click某个按钮(比如Button2): 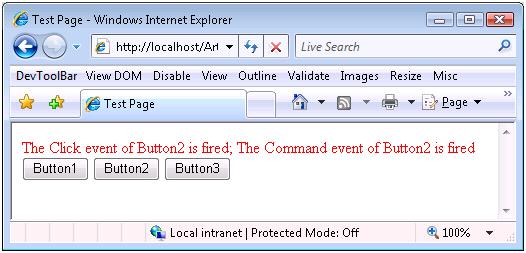 我们通过最上方的Message可以看出,Button2的Click Event和Command先后触发 。 这篇Blog的主旨就是从方法调用的角度讲述整个程序运行的过程:从HTML 被Render到Client端,到用户Click某个按钮,输入被Postback到Server端,并触发两个Event,执行Event Handler打印出相关的Message 。 首先我们来看看ASP.NET设计的Page Render到Client端的HTML是什么样子: 复制代码 代码如下: <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <title> Test Page </title> </head> <body> <form name="form1" method="post" action="Default.aspx" id="form1"> <div> <input type="hidden" name="__EVENTTARGET" id="__EVENTTARGET" value="" /> <input type="hidden" name="__EVENTARGUMENT" id="__EVENTARGUMENT" value="" /> <input type="hidden" name="__VIEWSTATE" id="__VIEWSTATE" value="/wEPDwUKMTA0NDQ2OTE5OWRk281L4eAk7iZT10hzg+BeOyoUWBQ=" /> </div> <script type="text/javascript"> <!-- var theForm = document.forms[form1]; if (!theForm) { theForm = document.form1; } function __doPostBack(eventTarget, eventArgument) { if (!theForm.onsubmit || (theForm.onsubmit() != false)) { theForm.__EVENTTARGET.value = eventTarget; theForm.__EVENTARGUMENT.value = eventArgument; theForm.submit(); } } // --> </script> <div> <span id="LabelMessage" style="color:Red;"></span> </div> <div> <input type="submit" name="Button1" value="Button1" id="Button1" /> <input type="button" name="Button2" value="Button2" onclick="javascript:__doPostBack(Button2,)" id="Button2" /> <input type="button" name="Button3" value="Button3" onclick="javascript:__doPostBack(Button3,)" id="Button3" /> </div> </form> </body> </html> |